Green Building Techniques for Tomorrow
As the world grapples with climate change and environmental degradation, the construction industry is turning towards green building techniques to create sustainable and eco-friendly structures. These techniques not only reduce the environmental impact of buildings but also provide healthier living spaces for occupants. Let’s explore some of the most innovative green building techniques for tomorrow.
What is Green Building?
Green building, also known as sustainable or eco-friendly building, involves designing and constructing buildings in a way that minimizes their environmental impact. This includes using sustainable materials, reducing energy and water consumption, and enhancing indoor environmental quality.
Benefits of Green Building
Why should we embrace green building? Here are some compelling reasons:
- Environmental Protection: Reduces waste, conserves natural resources, and lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
- Economic Savings: Decreases energy and water bills, and often qualifies for tax incentives and rebates.
- Health and Wellbeing: Improves indoor air quality and natural lighting, promoting better health for occupants.
Sustainable Site Selection
Choosing the right location is the first step in green building. This involves:
- Brownfield Redevelopment: Using previously developed land reduces the need to disrupt natural habitats.
- Public Transportation Access: Reduces the carbon footprint by encouraging the use of public transit.
- Site Orientation: Maximizing natural light and ventilation by positioning buildings appropriately.
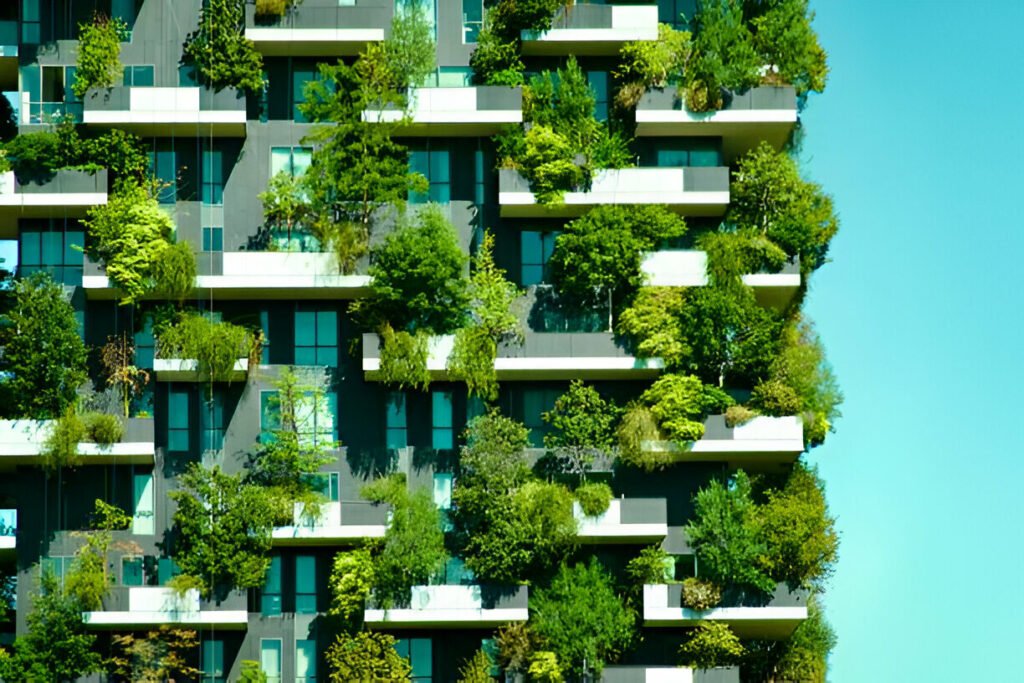

Energy-Efficient Design
Designing buildings to be energy-efficient is crucial. Techniques include:
- Insulation: Proper insulation reduces the need for heating and cooling.
- High-Performance Windows: These windows minimize heat loss in winter and keep interiors cool in summer.
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Using appliances with high energy star ratings reduces energy consumption.
Renewable Energy Integration
Incorporating renewable energy sources can significantly reduce a building’s carbon footprint. Options include:
- Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into electricity.
- Wind Turbines: Generate power from wind.
- Geothermal Systems: Use the earth’s heat for heating and cooling.
Water Conservation
Water conservation techniques itsreleased.co ensure sustainable water use. Strategies include:
- Low-Flow Fixtures: Reduce water usage without compromising performance.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collects and stores rainwater for non-potable uses.
- Greywater Recycling: Reuses water from sinks and showers for irrigation and flushing toilets.
Sustainable Materials
Using sustainable materials is a cornerstone of green building. Consider:
- Recycled Materials: Use materials that have been recycled or repurposed.
- Locally Sourced Materials: Reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
- Low-VOC Products: These products emit fewer volatile organic compounds, improving indoor air quality.
Indoor Environmental Quality
Ensuring a healthy indoor environment is key. Techniques include:
- Natural Ventilation: Uses outdoor air to reduce the need for mechanical ventilation.
- Non-Toxic Materials: Avoids materials that release harmful chemicals.
- Daylighting: Maximizes natural light, reducing the need for artificial lighting.
Waste Reduction and Management
Effective waste management minimizes environmental impact. Strategies include:
- Construction Waste Recycling: Recycling materials from construction reduces landfill use.
- Deconstruction: Carefully dismantling buildings to reuse materials.
- Composting: Organic waste from construction can be composted.
Green Roofs and Walls
Green roofs and walls provide numerous benefits, such as:
- Insulation: Helps regulate building temperature.
- Stormwater Management: Absorbs rainwater, reducing runoff.
- Biodiversity: Creates habitats for wildlife.
Smart Building Technologies
Smart technologies enhance building performance and sustainability:
- Automated Systems: Control lighting, heating, and cooling for optimal efficiency.
- Energy Management Systems: Monitor and manage energy use in real-time.
- Smart Thermostats: Adjust temperature settings based on occupancy and weather conditions.
Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design takes advantage of natural sunlight for heating and lighting:
- Orientation: Buildings are oriented to maximize sun exposure in winter and minimize it in summer.
- Thermal Mass: Materials that absorb and store heat during the day and release it at night.
- Shading: Uses overhangs and shading devices to block excessive sunlight.
Life Cycle Assessment
Life cycle assessment (LCA) evaluates the environmental impact of a building throughout its life cycle:
- Material Selection: Choosing materials with low environmental impact.
- Energy Use: Assessing energy consumption over the building’s lifespan.
- End-of-Life Disposal: Planning for recycling or repurposing materials at the end of the building’s life.